Strategic Growth.
Global Reach.
We guide investors and family offices through complex real estate, M&A, and international trade transactions.
Bridging the gap between complex international markets and motivated investors.
Established in 2020, Kakol Real Estate combines IT-driven due diligence with deep institutional knowledge to deliver exceptional value in every transaction.
Strategic Partners
Proven Results.
International Infrastructure Development

Successfully delivered a portfolio of top-tier projects, many with Gross Domestic Value (GDV) exceeding $500m and $1bn. These projects attracted significant international investment, validating our rigorous origination and vetting methodology.
Read Case StudyHigh-Volume Bitcoin Liquidation

The liquidation was completed within the required period, with zero market slippage and full regulatory compliance, securing the client's capital in fiat currency.
Read Case StudyCEE Hotel Divestment

Successfully identified a buyer and closed the transaction at the target valuation, allowing the seller to exit their investment with a solid return despite the challenging regional market conditions.
Read Case StudyReady to record your success?
Our methodologycal approach has delivered results for institutional clients worldwide. Engage us to structure your next high-impact transaction.
Selected Offers.
Semiconductor Startup

Series B growth equity for a leader in ultra-low power RISC-V silicon architecture.
With a secured pipeline of Tier-1 manufacturing partnerships and a modular IP core ready for deployment, they are now raising capital to accelerate global market penetration.
View Offer DetailsDiversified REIT Opportunity

Strategic allocation in an Exchange-listed REIT with diversified exposure to African and CEE assets.
Targeting substantial discounts to NAV (35-50%), this fund offers potential IRRs exceeding 20-25% over a 5-year realization horizon.
View Offer DetailsEU Coffee Importer

High-yield trade finance opportunity in the global coffee supply chain with shipping-insured returns.
Investors are offered a flat annual return of 18%, backed by insured shipments (110% of value) and contracted European buyers.
View Offer DetailsReady to secure a position?
Our offer tranches are limited and often fully committed ahead of market announcement. Contact us to reserve your allocation.
Investment Mandates.
Share-Backed Finance

Liquidity from public and private equity with LTVs up to 80%.
Interest rates range from 4% to 9% per annum. We enable quick liquidity with a streamlined due diligence process, ensuring absolute confidentiality.
View Mandate DetailsBuying Gold

Direct institutional procurement of physical gold bullion.
Every mandate is supported by a comprehensive logistics and security framework. We handle the assay verification, international transport, and secure vaulting coordination, ensuring that your capital is converted into physical wealth with absolute transparency and integrity.
View Mandate DetailsBuying Bitcoin

Institutional-grade acquisition and liquidation of large-scale digital assets.
Minimum transaction size is $1,000,000 USD. We support BTC, USDT, and FIAT pairs (EUR/USD) with same-day settlement options.
View Mandate DetailsReady to discuss a mandate?
We execute high-impact financial and resource mandates for global institutions. Structured for security, precision, and capital velocity.
Latest Insights.

The Future of Corridor Economics
Analyzing the structural shifts in global trade routes and the emergence of strategic investment blocs.

Institutional Adoption of Digital Assets
Why traditional family offices are moving towards large-scale Bitcoin mandates in 2026.
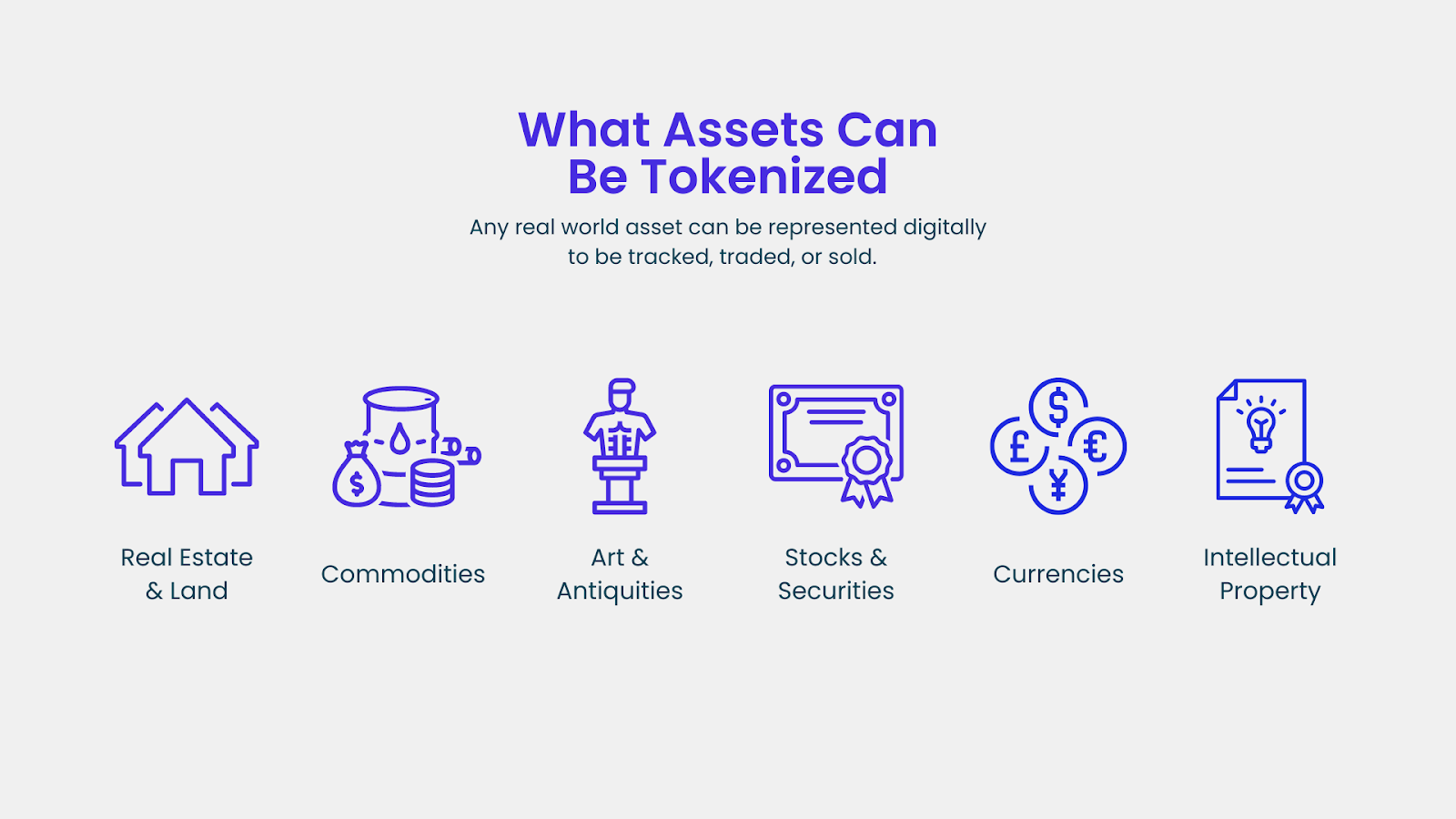
Tokenization: The Next Real Estate Frontier
How blockchain is democratizing access to institutional-grade commercial property portfolios.
Ready to secure your next strategic asset?
Join our network of international investors and gain access to vetted, off-market opportunities.